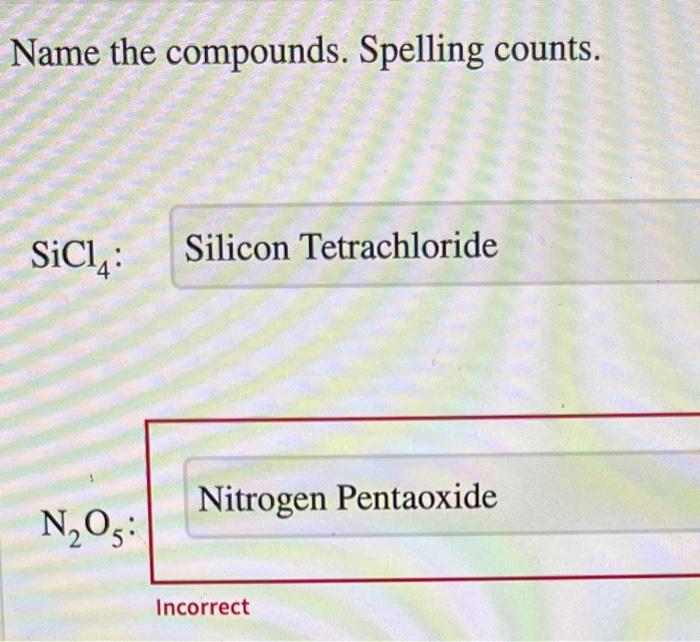
Embarking on the realm of chemistry, we encounter the crucial task of naming compounds. name the compounds. spelling counts. delves into the intricacies of chemical nomenclature, emphasizing the significance of precision in representing molecular structures.
This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and understanding to confidently identify and name a wide range of chemical compounds, ensuring clear communication and accurate documentation within the scientific community.
Naming Compounds

In chemistry, naming compounds is an important skill that allows us to identify and describe chemical substances. There are various systems for naming compounds, each with its own rules and conventions. In this article, we will explore different methods for naming inorganic and organic compounds.
Naming Inorganic Compounds, Name the compounds. spelling counts.
Inorganic compounds are typically composed of metals and non-metals. The following guidelines can be used to name inorganic compounds:
- Cations(positively charged ions) are named first, followed by anions(negatively charged ions).
- For monatomic cations(cations formed from a single atom), the name of the metal is used. For example, Na +is named sodium ion.
- For polyatomic cations(cations formed from multiple atoms), the suffix “-ium” is added to the root name of the central metal. For example, NH 4+is named ammonium ion.
- For anions, the suffix “-ide” is added to the root name of the non-metal. For example, Cl –is named chloride ion.
- For polyatomic anions, the suffix “-ate” is used for the most common anion of an element, and the suffix “-ite” is used for the less common anion. For example, SO 42-is named sulfate ion, and SO 32-is named sulfite ion.
Naming Organic Compounds
Organic compounds are typically composed of carbon and hydrogen, and may also contain other elements such as oxygen, nitrogen, and halogens. The following guidelines can be used to name organic compounds:
- Alkanes(saturated hydrocarbons) are named based on the number of carbon atoms in the chain. The suffix “-ane” is added to the root name of the alkane. For example, CH 4is named methane.
- Alkenes(unsaturated hydrocarbons with one double bond) are named based on the number of carbon atoms in the chain. The suffix “-ene” is added to the root name of the alkene. For example, C 2H 4is named ethene.
- Alkynes(unsaturated hydrocarbons with one triple bond) are named based on the number of carbon atoms in the chain. The suffix “-yne” is added to the root name of the alkyne. For example, C 2H 2is named ethyne.
- Alcohols(compounds containing an -OH group) are named based on the number of carbon atoms in the chain. The suffix “-ol” is added to the root name of the alcohol. For example, CH 3OH is named methanol.
- Carboxylic acids(compounds containing a -COOH group) are named based on the number of carbon atoms in the chain. The suffix “-oic acid” is added to the root name of the carboxylic acid. For example, CH 3COOH is named ethanoic acid.
Top FAQs: Name The Compounds. Spelling Counts.
What is the importance of naming compounds correctly?
Accurate naming of compounds is essential for unambiguous identification, clear communication, and ensuring safety in handling and storage.
How can I learn to name compounds effectively?
Practice and consistency are key. Utilize resources such as textbooks, online databases, and interactive tools to reinforce your understanding.
What are the common mistakes to avoid when naming compounds?
Pay attention to spelling, prefixes, and suffixes. Ensure that the name accurately reflects the molecular structure and charge, if applicable.